Insights > Category > Posted: 2025-Mar-21, Updated: 2025-Mar-31
Energy Star Labels
Understanding Ratings
Energy Star Certification
The Energy Star symbol indicates that a product meets or exceeds high-efficiency standards. Currently, more than 70 product categories can qualify for the symbol, and typically, a certified model is in the top 15 to 30 percent of its class for energy performance.
Every ENERGY STAR® certified window, door and skylight is required to leave the factory with a removable label that shows:
- its certified performance ratings (U-factor, Energy Rating, etc.)
- the climate zone(s) for which it is certified
- a description of the product (type, materials, glazing, etc.)
- its certification information
Energy Rating (ER)
The Energy Rating (ER) for window products is an evaluative rating made by an authorised neutral organisation. All products are assessed using a strict common procedure. A window’s ER rating is a measure of its overall performance, based on the three factors below:
- solar heat gain
- heat loss through frames, spacers, and glass
- air leakage heat loss
Higher is better - the higher the rating, the better the performance.
U-Value (U-factor)
The U-value refers to a measure of the heat gain or loss through glass due to the difference between indoor and outdoor air temperatures. It describes how well a product prevents heat from escaping a home or building. U-value ratings generally fall between 0.2 and 1.2. U-factor is particularly important during the winter heating season.
Lower is better - the lower the U-value, the better the product is at keeping heat inside the home.
R-Value
The R-value represents the resistance a material has to heat flow. It measures the effectiveness of insulation in stopping heat flow.
Higher is better - the higher the R-value, the greater the heat resistance.
CR-Value
The CR-value indicates how well a product resists the formation of condensation (Condensation Resistance). CR is reported on a rating scale of 1 to 100.
Higher is better - the higher the number, the better a product is at resisting condensation.
Air Leakage (AL)
Air leakage measures how much air passes through cracks in the window assembly. It is particularly relevant in cold climates, as lower values indicate better air sealing, reducing drafts and heat loss.
Lower is better — a lower AL reduces energy loss and drafts, keeping your home warmer.
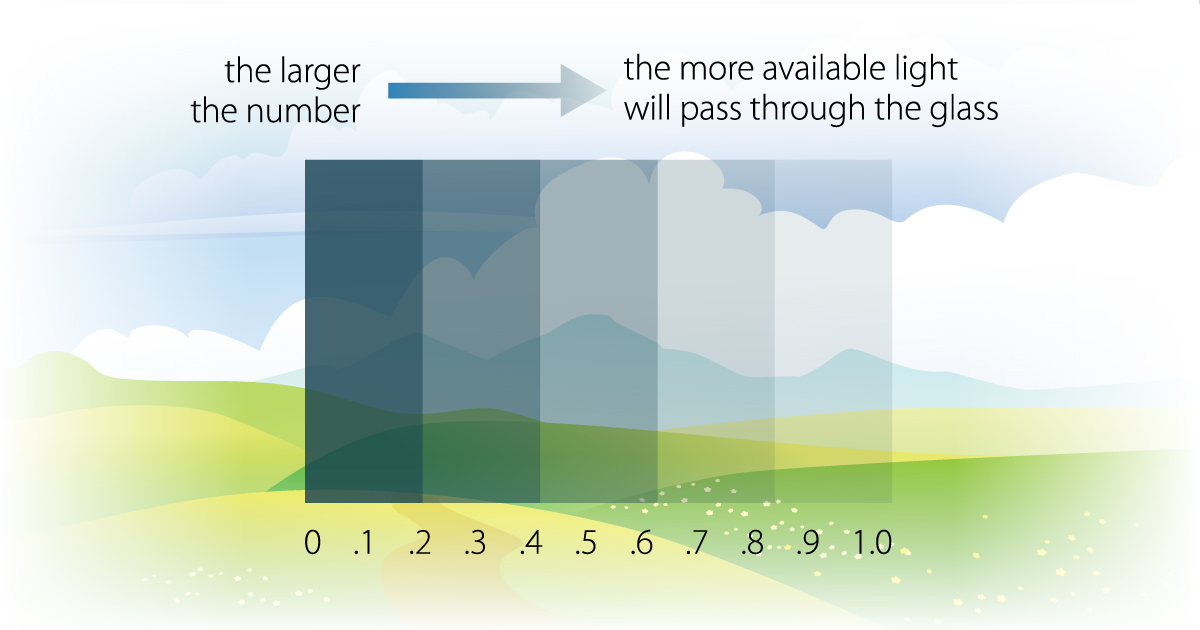
Visual Transmittance (VT)
Visual transmittance (VT) indicates the amount of light in the visible portion of the spectrum that passes through a glazing material. A higher VT can maximize natural daylight, reducing the need for artificial lighting, while a lower VT reduces glare and can limit unwanted heat in warmer months.
Higher is often preferred — a higher VT allows more daylight, which can minimize the need for artificial lighting, especially in colder climates where maximizing sunlight can also help passively warm the home. However, in warmer months, too much light can contribute to overheating, so a balance may be needed depending on seasonal conditions.
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC)
The SHGC is a measurement of the heat transmitted and absorbed and subsequently released inward. SHGC is expressed as a number between 0 and 1. In colder climates like Ottawa, a higher SHGC may be beneficial for capturing solar heat in winter, while a lower SHGC helps keep homes cooler in summer.
Climate-specific: In colder climates, a higher SHGC may help capture warmth, whereas in hot climates, a lower SHGC helps reduce heat gain.
Related stories
Ready to enhance your home's energy efficiency?
Whether you’re looking to better understand window and door ratings or need expert guidance on choosing the best options for our Ottawa area climate, we’re here to help. Give us a call, fill out our contact form, or visit our showroom to discover the perfect energy-efficient solution for your home!
Efficient - INFOGRAPHIC
INFOGRAPHIC
Understanding Ratings
CDN Climate Zone
Comparing Products
Visual Transmittance (VT)
Solar Heat Gain (SHGC)
Energy Star (ER)
Air Leakage (AL)
R-value of Insulation
U-factor (U-Value)
Spectrally Selective Coatings
Low-E Coatings
Gas Between the Panes