Insights > Category > Posted: 2025-Mar-21, Updated: 2025-Mar-31
Performance Rating
U-factor (U-Value)
What is a U-Factor?
The U-factor (or U-value) is a key measure of a window's insulating properties. The lower the U-value, the better the window is at keeping heat inside during winter and preventing heat from entering during summer. In Ottawa, where temperatures can vary dramatically, understanding U-values is crucial for optimizing home comfort and energy efficiency.
Measuring heat transfer through windows
The U-factor measures the overall heat transfer through a window due to differences between indoor and outdoor temperatures. It’s also known as the overall coefficient of heat transfer. U-value ratings generally range from 0.20 to 1.25, with lower values indicating better insulation.
When evaluating windows, it’s important to consider the U-value for the entire window assembly, including the frame, edge seals, and glass. The frame and edges typically have higher U-values than the centre of the glass, so make sure you are looking at the U-value for the whole window unit.
Why U-Factor matters
Most manufacturers provide U-values for the entire window, but some may not. Energy Star certification provides a reliable U-factor rating for windows, ensuring they meet specific energy efficiency standards.
While energy costs for heating are typically higher than for cooling, improving your windows' insulation helps reduce both heating and cooling expenses. The smaller the U-value, the better the window performs in keeping heat inside during winter and minimizing heat gain during summer.
U-Factor Summary for Ottawa:
- Lower U-value: Better insulating properties, leading to improved energy efficiency and comfort.
- Key Benefit: Helps retain heat in winter and keep heat out in summer, ultimately reducing energy bills.
Related stories
Understanding U-factor and SHGC for better window choices in Ottawa
By understanding both U-factor and SHGC, you can choose windows that offer optimal performance for your home’s specific needs. Consult with a window specialist to find the best options that balance insulation and solar heat management for your climate.
Efficient - INFOGRAPHIC
INFOGRAPHIC
Understanding Ratings
CDN Climate Zone
Comparing Products
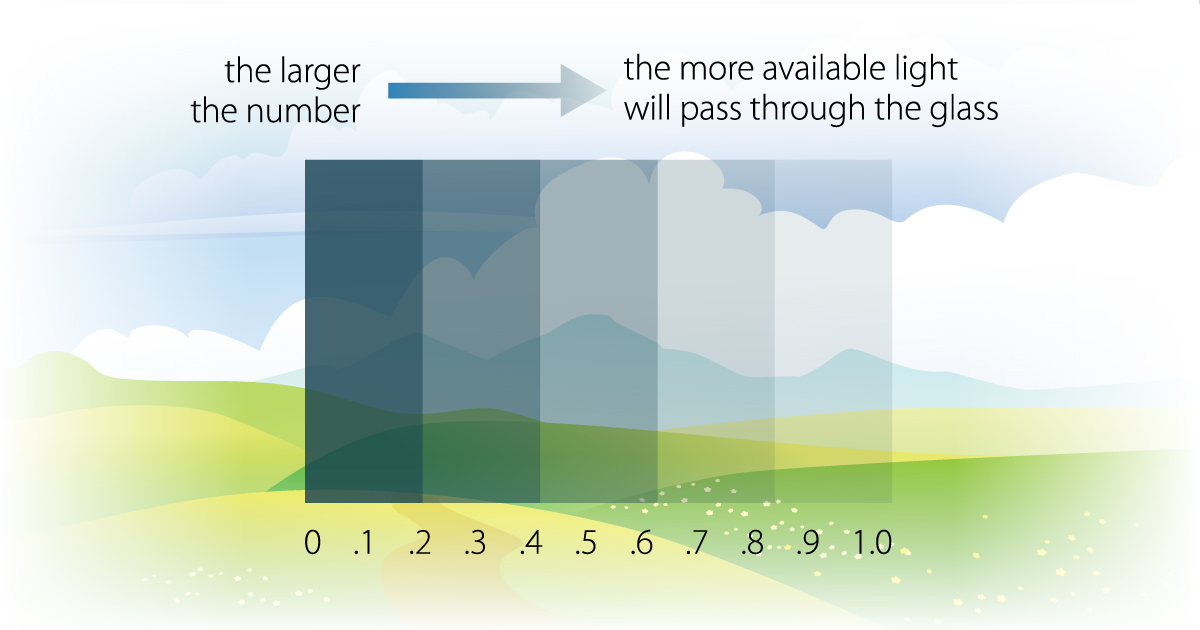
Visual Transmittance (VT)
Solar Heat Gain (SHGC)
Energy Star (ER)
Air Leakage (AL)
R-value of Insulation
U-factor (U-Value)
Spectrally Selective Coatings
Low-E Coatings
Gas Between the Panes